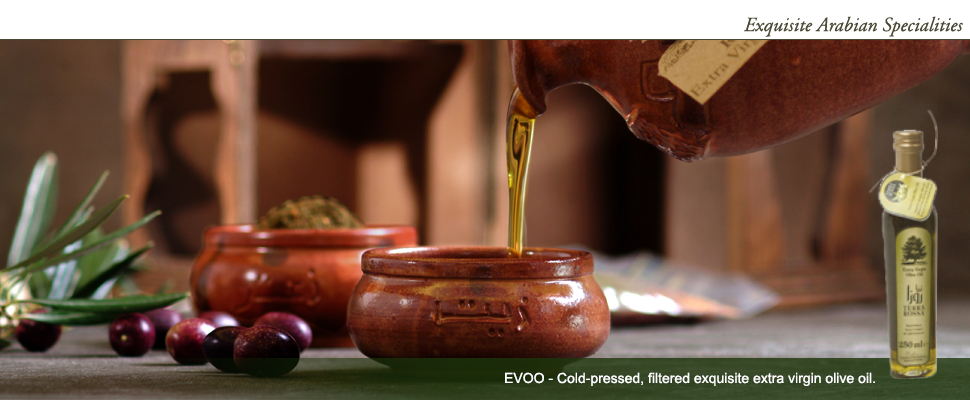
Benefits of Olive Oil
Olive oil is an integral part of the "Mediterranean diet" which is associated with sensible tasty portions and slower, more enjoyable eating. People who eat a "Mediterranean diet" have been shown to have a remarkable variety of health benefits. Olive oil can quickly satisfy hunger and lead to fewer total calories ingested at mealtime. Studies suggest that olive oil decreases rates of cardiovascular disease and cancer. It is unclear if any single component of olive oil is responsible for these health benefits or if it is a combination of olive oil and a diet high in vegetables, fruit and fish.
Extra virgin olive oil is one of the few oils that can be eaten without chemical processing. (Nearly every other vegetable oil has not been detoxified and refined with steam and solvents). Fresh pressed olive oil can be eaten immediately and retains the natural flavours, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and other healthy products of the ripe olive fruit.
Most doctors advocate lowering total fat and calories in your diet, and substituting butter, margarine and tropical oils with healthy fats like olive oil.
The Antioxidant Activity of Polyphenols Has Shown Promising Results with Respect to:
Atherosclerosis
Oxidized low-density lipoproteins (LDL) contribute to the progression of human atherosclerosis. Antioxidants have been shown to prevent LDL modification. The beneficial effects of a Mediterranean diet may be defined by the unique antioxidant properties of its phenolic compounds.
Antimicrobial Activity
Olive polyphenols have been demonstrated to inhibit or delay the rate of growth bacteria such as Salmonella, Cholera, Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas, and Influenza in vitro. These data suggest a potential role of olive water polyphenol antioxidants in promoting intestinal and respiratory human and animal wellness, and as an antimicrobial food additive in pest management programs.
Cancer
There is a growing body of evidence that reactive oxygen species are involved in the etiology of fat-related neoplasm, especially in patients suffering from predisposing inflammatory conditions where high quantities of reactive oxygen are produced. Recent studies have shown that the abundant phenolic antioxidant fractions of olive oil have a potent inhibitory ability on reactive oxygen species associated with colon and breast pathologies.
Oxidative Stress from Passive Smoking
Recent studies which involve administration of the phenolic fraction from olive water in rats exposed to oxidative stress from secondary smoke, show a dramatic reduction of stress and protective activity by polyphenols in the diet.
Skin Damage and Photoprotection
The skin damage produced by overexposure to sun rays and environmental stress is related to the destructive activity of free oxygen related radicals produced by skin cells. Polyphenolic components of olive oil have been compared to traditional antioxidants, such as tocopherols, used by the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industry to prevent skin damage. Results show polyphenols as having the highest activity as radical scavengers.